Enterprises are considered to be rural-impacting if they engage positively in commerce in rural areas and improve access to goods, services and/or markets. Many of these rural-impacting enterprises are micro, small and medium-sized enterprises (MSMEs), which, according to the Center for Strategic and International Studies, make up the most significant percentage of businesses in the private sector.
In recent years, there has been growing interest in rural enterprise development. This is no surprise as these organizations play a critical role in achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) as they contribute to creating jobs and reducing poverty.
Factors such as a lack of infrastructure, limited access to finance, and markets have made it difficult for rural businesses to access dedicated support that could cater to their unique needs and enable their progress. Many entrepreneurs in Sub-Saharan Africa that run rural enterprises are locked out of existing entrepreneur support interventions due to their limited education, skills, lack of knowledge about available resources, as well as cultural and social barriers.
That said, there are Entrepreneurial Support Organizations (ESOs) working to provide support ranging from business planning and modeling to investment readiness. However, these support organizations are equally siloed from the ecosystem and often need as much support as the entrepreneurs they support.
In 2022, Village Capital and Small Foundation launched an ecosystem research initiative working to identify gaps, synergies, and opportunities for exponential impact within the rural impacting enterprise (RIE) ecosystem in sub-Saharan Africa. This first-of-its-kind research aims to give stakeholders an understanding of where and how to focus their ecosystem support efforts most effectively. We received 188 applications for the initiative and used data from those applications to put together a snapshot of the RIE ecosystem landscape in Sub-Saharan Africa.
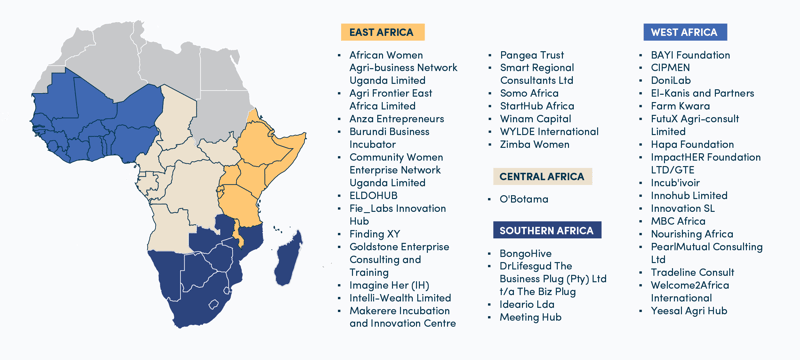
Here’s what we have learned:
Most ESOs operate with small operational budgets. 147 ESOs (80 percent) report an operating budget under USD 500,000, and only 4 (2%) of ESO applicants report an annual operating budget of over USD 2 Million.
East Africa has the leading number of ESOs supporting RIEs. 60 percent of the ESOs that applied have operations in East Africa, followed by West Africa at 42 percent. Up to 46 percent of applicants (ESOs) report that over 50 percent of their clients are rural businesses.
ESOs are not only focusing on rural enterprises. Most ESOs support high-growth ventures that have highly innovative business models serving large addressable markets, with a rapid growth trajectory. These enterprises are more likely to have a higher likelihood of survival and return on investment. Rural enterprises are often livelihood-sustaining enterprises. They are much smaller in size, falling under the micro-enterprises category. While ESOs are working to support them to become more formalized ventures, they are not always the primary support target.
Most rural enterprises are in the agriculture sector. This comes as no surprise. Agriculture is the leading economic activity in sub-Saharan Africa. In addition, many of these enterprises are youth-led and women-led, which is consistent with the demographics in the region. According to the MasterCard Index of Women Entrepreneurs (MIWE), Sub-Saharan Africa has the world's highest rate of women involved in entrepreneurial activity at 26 percent.
ESOs are more focused on developing hard skills. Hard skills encompassing financial and business management are critical in business. We found that the majority of the ESOs (80 percent) focused on providing training on developing hard skills through acceleration and incubation. Soft skills were equally prioritized and we found that 66 percent of the ESOs provided an opportunity for networking and market linkages. Mentoring and coaching are also popular offerings.
Most ESOs are donor funded and grant-reliant. 36 percent of the ESOs operate as non-profits while 40 percent have a hybrid structure, operating as non-profits that earn revenue or for-profits that have a very strong social mission.
The ESO sector in Africa is heavily financed by grant funders with 36%of the ESOs operating as non-profits while 40 percent have a hybrid structure, operating as non-profits that earn revenue or for-profits that have a very strong social mission.
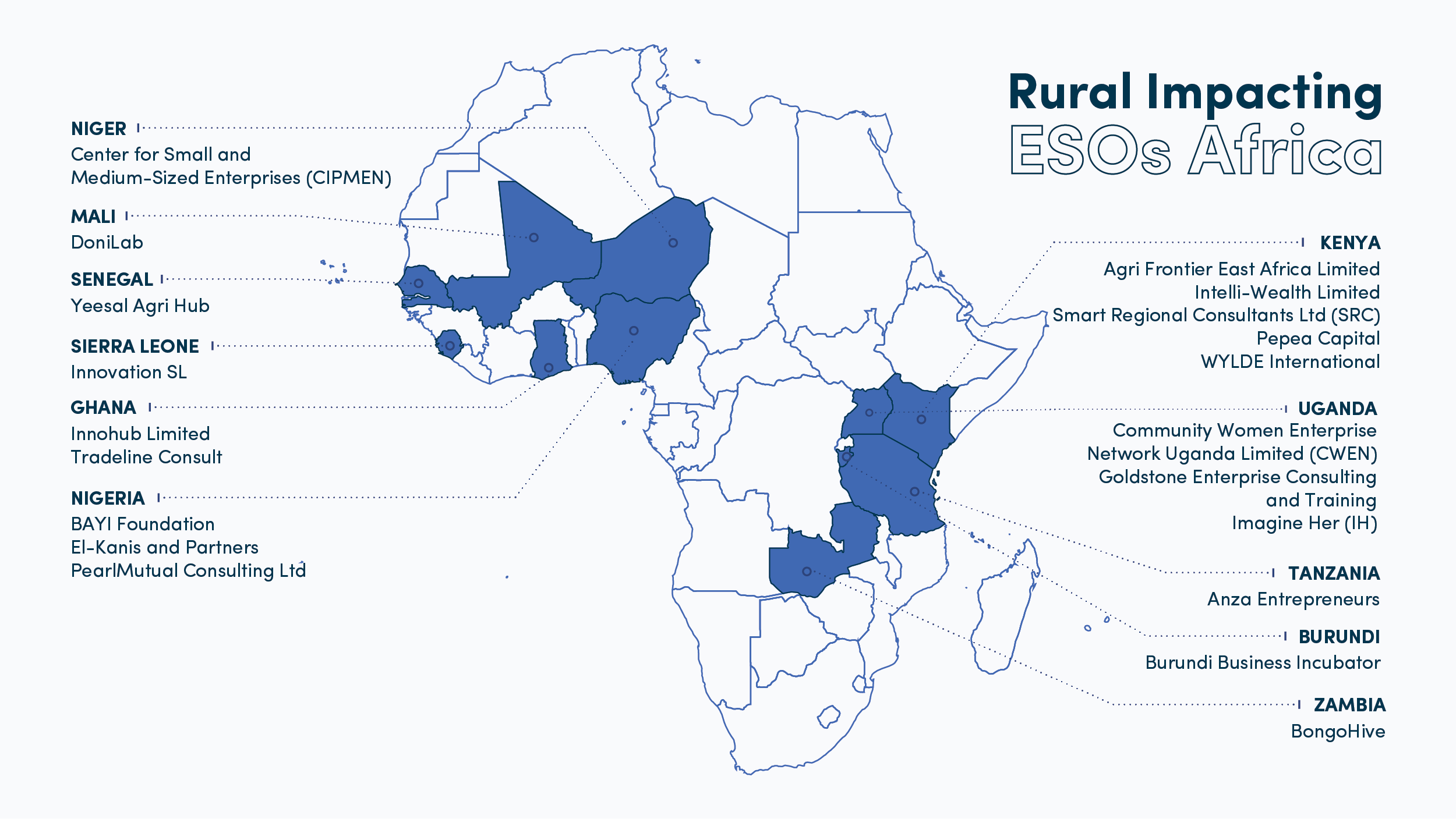 Here are the selected ESOs:
Here are the selected ESOs:
Our newsletters share the latest about our programs, trends, ecosystem leaders, and innovative entrepreneurs in the impact world. Get the latest insights, right in your inbox by subscribing:
Village Capital needs the contact information you provide to us to contact you about our products and services. You may unsubscribe from these communications at any time. For information on how to unsubscribe, as well as our privacy practices and commitment to protecting your privacy, please review our Privacy Policy.